In this web we explain various methods of dewatering foundation excavation like sump pumping, Deep well construction method, freezing method of dewatering, chemical consolidation methods of dewatering, cement grouting method of dewatering, well point method of dewatering, electro-osmosis. also share necessity of dewatering, definition of dewatering, in which situation dewatering methods are use and so more explain in detail.
Table of Contents
What is Dewatering
If water is leaking into the trench during foundation excavation, it is very important to dispose of it. If water is not removed from the trench, it is difficult to make concreting or masonry in the foundation. And the concrete or masonry becomes weak. The action of removing water from the underground construction (mostly for foundation), is called dewatering.
Necessity of dewatering in Construction
- Ease of concreting or masonry in foundation.
- To protect concrete or masonry from the effects of water.
- To prevent soil erosion around the base (pit).
In which situation dewatering is required?
Dewatering is required for the safety of the structure around the pit in the following conditions:
- Deep excavation
- Construction in water logged area
- Docks
- Pile Foundation
Also Read: What is Slurry Wall Construction?
Methods of Dewatering
The various methods of dewatering are as follows:

- Sump Pumping
- Deep well construction method
- Freezing
- Chemical consolidation of soils
- Cement Grouting
- Well point system.
- Electro-osmosis
1. Sump Pumping

In this methods of dewatering water is disposed by adjusting the pump of the trench. Centrifugal pumps are generally more useful.
This method is used for shallow bases in waterlogged areas. In this way ditches are dug on both sides of the trench. The ditches size is usually 20 cm in diameter of a semicircle.
Sumps are made at a distance of 40 m to 60 m in the ditches. The size of the Sumps (latch) is kept as 1m x 1m x1m. The water flows into the ditches and collects in the Sumps. Water is pumped out from the Sumps continuously.
Also Read: Different Causes of Foundation Failure
2. Deep well construction

This methods of dewatering is more suitable when digging operation (digging trench) is lower than water table or artesian water present in soil. This method is useful when the groundwater level needs to be lowered further.
3. Freezing methods of dewatering
- In this method, 15 to 60 cm diameter casing pipe is lowered into the ground.
- A suitable mesh or filter layer is placed at the bottom of the casing.
- At the bottom of the casing is a submersible pump inserted.
- The pumping capacity should be 30 cm or more.
- When the depth of excavation is greater and the area of excavation is greater, deep wells are constructed at appropriate distances from the edge of excavation every 10 m to 30 m depending on how low the groundwater level has to be lowered.
- A separate pump is kept for each well.
- A well point necklace is also arranged along the slope of the deep excavation.
Also Read: How to construct Foundation in Black Cotton Soil
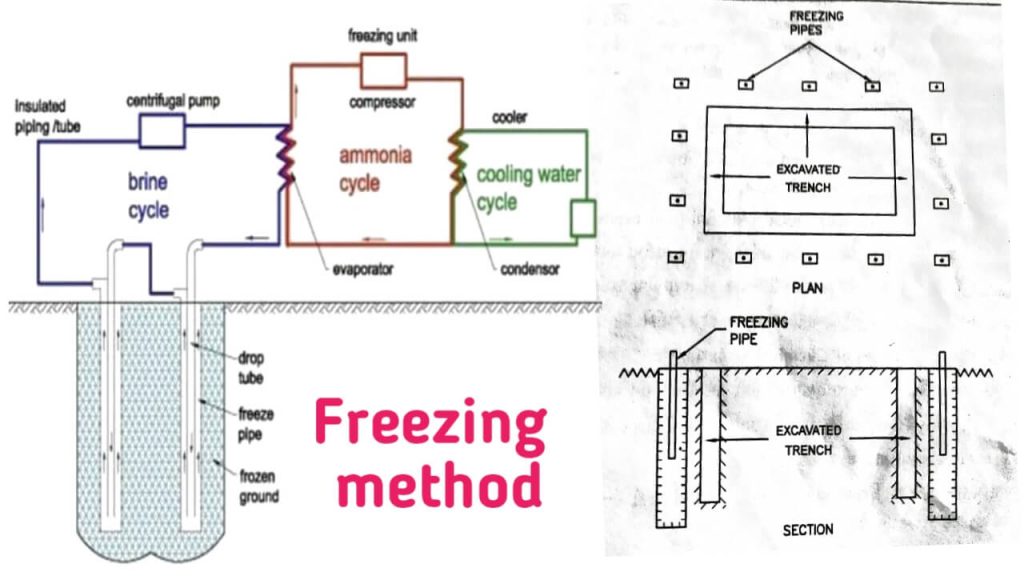
In this methods of dewatering, a wall of frozen clay is made by, freezing the moist soil of the area where the excavation is to be carried out.
The process of freezing method of dewatering is as follows:
- Large pipes of 10 to 15 cm diameter are laid in the ground around the area where excavation is to be done.
- The spacing between such pipes is 1 to 1.5 m.
- These pipes are closed at the lower end.
- Small pipes of 5 cm diameter are laid, which are open or perforated at the lower end.
- The upper ends of all small pipes are connected to the refrigeration plant by a single pipe.
- In these small pipes, 23°C to 30°C cold water or other liquid is circulated.
- Coldwater escapes from a small pipe and climbs up into a large pipe and returns to the refrigeration plant.
- This cold water freezes the moist soil and forms a wall of frozen clay.
The following precautions should be taken in the method of freezing:
- The freezing area should be as small as possible. If the area is large, advantage of Arch action can be taken by arranging the pipes in a circle. If the area is small, the pipes should be arranged rectangularly or squarely.
- Frozen clay wall should extend to the impervious layer below the ground.
- This method is effective only for water-bearing sand, gravel or alluvial soils.
- This method is suitable only for short term works, as operating cost is very high in this method and the stability of frozen soil is not long lasting.
- This method is very expensive, so it should be used only when dewatering cannot be done in any other way.
Also Read: What is Autoclave Aerated Concrete
4. Chemical consolidation of soils
- In this methods of dewatering, the soil around the area to be excavated is hardened with a solution of chemical compounds like silicate of soda and calcium chloride.
- In this method also pipes are lowered into the ground. When a pipe is lowered into the ground, a chemical is forced into it.
- The first chemical insertion is done after the pipe reaches the appropriate depth.
- The pipe is then slowly pulled out and at the same time another chemical is forcibly inserted into the pipe.
- The chemical reaction between these two chemicals makes the soil hard. This method is very costly.
The following points should be kept in mind while choosing chemicals.
- Chemicals should be able to improve soil properties. This should increase the strength of the soil and reduce the permeability.
- Chemicals should be cheap, non-toxic, non-explosive.
- Chemicals should be in low viscosity liquid form so that they can be easily inserted into the soil.
- Chemicals should not be chemically reacted with pipes or pumps.
- The chemicals should be free from impurities in soil and water.
Advantages of Chemical Grouting:
- It hardens in cold and hot environments, so it can be used at any temperature.
- It can be used to close narrow cracks up to 0.05 mm wide.
- Its viscosity is equal to the viscosity of water. So chemical grout can be ejected into the soil in which water can be ejected.
- Some chemicals have great strength like polyester resin have a compressive strength of 1400 kg/cm2 and a tensile strength of 360 Kg/cm2.
Also Read: Different Types of Partition wall
5. Cement grouting

- Cement grout is used in this methods of dewatering. Cement grout is a mixture of cement, sand and, water.
- In this process several holes are made in the ground. Cement grout is forcibly inserted into each of these holes.
- The grout is filled in the hall until the grout comes out of the hall.
- Cement grout freezes in stone cracks and clay cavities, making the stone or clay water-tight and monolithic.
The following points should be kept in mind in case of grouting:
(a) Holes:
There are no standard rules for depth, diameter, spacing of holes. The depth, direction, bending angle, etc. of the hole varies according to the type of stone.
(b) Cement grout:
Cement grout should be easily workable and uniform. Generally 30 to 90 liters of water is used for 1 bag of cement. The grout should not contain cement lumps. Grouting pressure should be maintained according to the cracks in the stone. Portland cement grout is only useful for cracks up to 1.6 mm wide.
Grouting in soft soil:
Minimal channels of resistance are prepared before starting grouting in soft soil. For this at a short distance two bottom perforated pipes are pushed into the soil and water is forcibly inserted in one of them and water is forcibly inserted in the first pipe till water appears in the other pipe.
In this way, minimum barrier channel is formed between the two pipes. In this way many other minimal barrier channels are formed in the soil.
Then the cement slurry is forcibly inserted in the pipe through which the water has inserted.
Is inserted by force and the cement slurry is continued to be inserted until a cement slurry appears in the second, perforated pipe.
This is how a waterproof layer is formed by forcibly inserting grout into the soil around the channel. And that way the springs of water in the base trenches can be stopped.
Also Read: Types of Geosyntehtics material
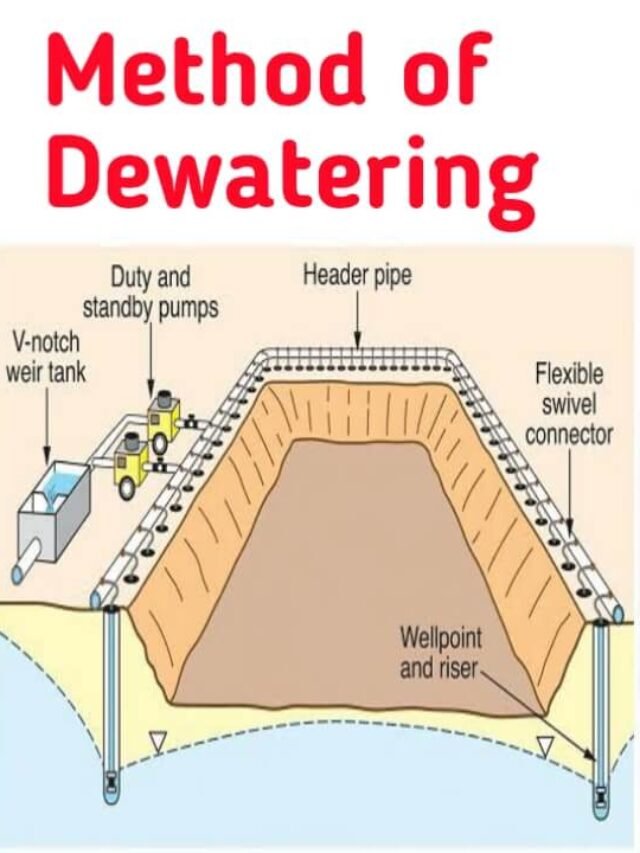
6. Well Point System of Dewatering
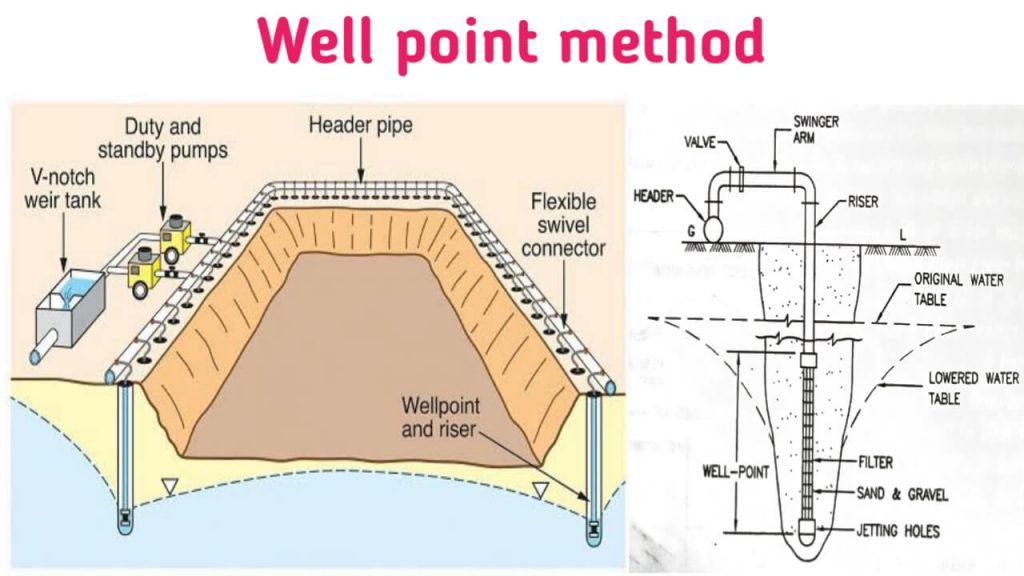
In this methods of dewatering the ground water flow is diverted into deep well-points in the ground and the part to be excavated is kept free from ground water.
Well points are prepared at a distance of about 1m around the area to be excavated.
The important parts of a well point system are as follows:
(a) Well point:
- A well point is a pipe whose length is approx. 1m and have a diameter of 40 mm to 50 mm.
- The well point has a valve at the bottom end which opens when water is forced into the pipe and closes when suction occurs.
- The in-flow pipe is perforated and has a thin mesh around it.
(b) Riser:
- A riser is a vertical pipe lowered into the ground with a well point at the bottom.
- Risers range in diameter from 40 mm to 50 mm.
(c). Swinger arm:
The pipe that connects the riser to the header is called swinger arm.
(d) Header:
A header is a pipe with which the Swinger arm of different well points are connected. The header pipe is finally connected to the pumping unit. The header pipe is arranged on the ground. They range in diameter from 15 cm to 25 cm.
Procedure of Well Point System:
The following Procedure is adopted in the well point:
- Well points are prepared at a distance of about 1m around the area to be excavated.
- Water is released at the rate of 20 to 25 liters per second at these well points, which causes the soil to be dug and the well point to sink deeper into the ground.
- The water edge is maintained for a short time even after the well point has reached the prescribed depth. This creates annular space around the well point as the water rises.
- The water flow is then stopped and filtered material like sand and gravel is filled in the annular space around the well point which stops the filling of soil particles as well as debris at the well point.
- Well – points are attached to the header with riser, tee-piece, and Swinger arm.
- The header pipe is paired with a suction pump to create a vacuum in the well-point and riser, so that water from the surrounding land enters the header through the well-point and descends to the ground water table.
Types of well-point system
There are three types of well point system:
- Single stage system
- Multiple stage system
- Vacuum System
1. Single stage system
Water can be lifted from a depth of 5 m with a suction pump. Therefore this method is used where the depth of excavation does not exceed 5 m. The plant is not disturbed until the excavation work is completely completed.
2. Multiple stage system
When excavation depth is more than 5 m below ground level (W.T.), well-point system is done in phases.
In the first stage excavation is carried out to a depth of 5m by arranging the required well-points. In the second stage additional well points are dug into the ground and excavated to a further depth of 5m. This is a way, how well-points are arranged and excavated to a greater depth. The sides of the excavation are given a proper slope.
Precautions to be taken in well point system
Pumping rate
Pumping rate should be higher than the flow rate of water coming from the surrounding land, Which causes early water table can be lowered.
Connections
All well-point connections should be air tight.
Air lock
The slope of all pipes should be kept in the direction of the pump set so that no air lock is created.
Deep-well pumps
Multiple well point systems should use deep well pumps when the slope of the excavation sides is not stable. Such pumps should be used only for important works as they are expensive.
Stand by pumps
To keep additional stand by pump set so that the work does not get stuck due to pump malfunction
7. Electro – Osmosis Method of Dewatering
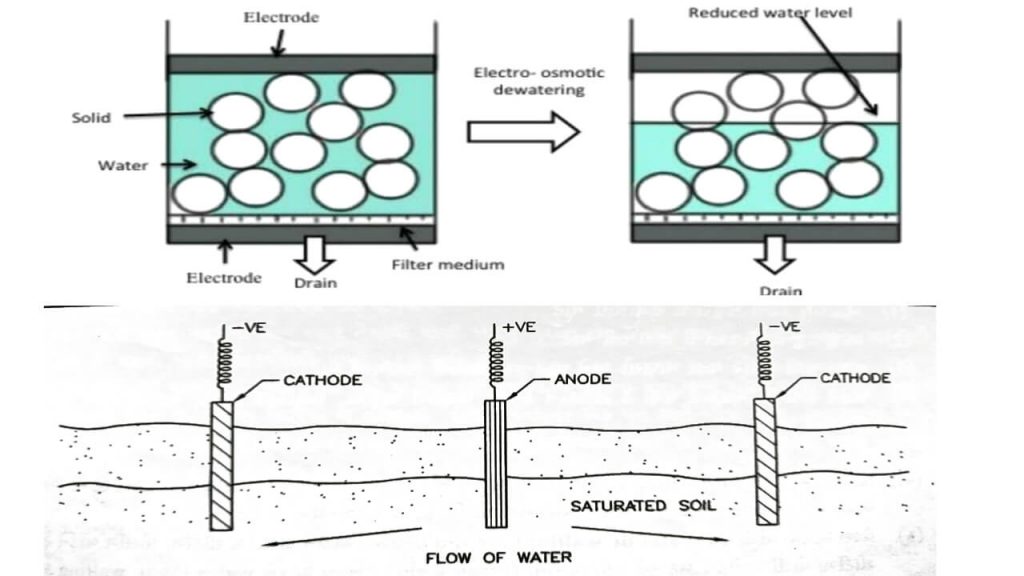
- When the soil is microscopic, it is difficult to draw water from it, as the permeability of such soils is very poor. Such soils hold water by capillary.
- The electrical properties of the water in the cavity, between the soil particles are used to dispose of water from such soils.
- In saturated soil, two electrodes, one positive and the other negative, are lowered.
- A direct current is passed between these two poles.
- The water in the soil is repelled by the anode and is attracted by the cathode.
- Cathodes are keep in well-points.
- Water stored near the cathodes well. This water are removed by pumping.
- This way the water level in the ground can be lowered.
- This method is suitable for dewatering in silts, clayey silts, fine clayey silty sands.
- The removal of water from the soil increases the stability of the slope and increases the shear strength of the soil.
Methods of Dewatering Quick Details Stories
Frequently Asked Questions on Dewatering
What are the different methods of Dewatering?
1. Sump Pumping
2. Deep well construction method
3. Freezing
4. Chemical consolidation of soils
5. Cement Grouting
6. Well point system
7. Electro-osmosis
What is Dewatering in civil engineering?
Dewatering is a method to remove Ground water from trenches. Generally, during excavation of foundation, Groundwater will come in trenches of foundation, it is necessary to water from trenches to construct foundation. In this conditions various dewatering methods is used to remove water.
When Deep Well system of Dewatering is preferred?
Deep well system of Dewatering is preferred when digging operation of trench is lower than water table or artesian water present in soil.
Dewatering Methods PDF Download
Download Dewatering methods pdf
Join Our Telegram Channel for more such useful information as soon as possible.
Also read:


it was very helpful…..we are greatful
Thank you very useful
Can I get this notes in pdf
You Can Easily Print It. Or Print This Details in form of PDF.
SMART MOTOR CONTROL PANEL
SINGLE & THREE PHASE (DOL & Star Delta, upto 100 HP)
Application: Dewatering, Commercial, Residential, Industrial etc.
FEATURES/ PROTECTIONS
Over load Programming.
Under load Programming. (Dry run)
Under voltage Programming.
Over voltage Programming.
Single phase preventer
Reverse phase protection
Unbalance voltage protection
Auto/manual mode selector switch
Inbuilt MCB /MCCB for input supply
Hour meter to show the total time of run
Digital Amp. & volt meter inbuilt
Auto switch inbuilt with Start delay time
Wide Voltage range; 170-470 VAC
Fabricated with powder coated G.I Sheet.
Continuous running capacity: 100 hrs.
How can i print this details in form of Pdf
you can directly print the full page by ctrl+p shortcut of computer.
Are there any books that go into this topic more in depth? I would like to learn more.
Nice clarification thanks
greetings, notable blog on lardy loss. comparable helped.
Actually you satisfied me
Hi.. can any body advice that, which methods of dewatering system is commonsly using for substation building construction works in Gulf Region? Since my client is going to construct their buidling from the depth of 5 mtr from the ground level they told us to propose the suitable dewatering system methods to us. The work location is in Kuwait region (in the Middle East). Expecting better advice from experience hand(s). Regards
I need to remove rain water that
collects behind a seawall on an
inland lake with a steep slope leading
to the seawall. Could i drive well
points down to the water table, about
5’ down and have them drain the water down?