In this article, we explain the classification of roads in India, based on pavement, carriageway, location, function, traffic, 20 year third road development plan, urban roads, etc.
Table of Contents
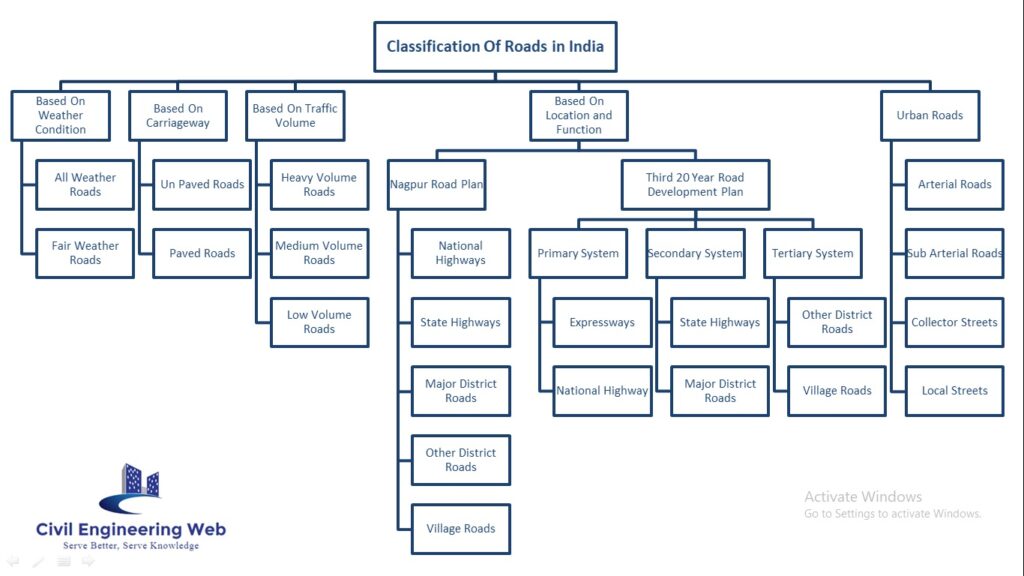
Classification of Roads
The different types of roads in india are classified as below.
- Based on Weather Condition
- Based on Carriageway
- Based on Traffic Volume
- Based on Nagpur Road Plan
- Based on Third 20 Year road Development Plan
- Urban Roads
Classification of Roads based on Weather Condition
The classification of roads based on weather condition are mentioned below.
- All Weather Roads
- Fair Weather Roads
All Weather Roads
All Weather Roads is defined as the road which is useful in ever seasons of the year except at major river crossing where some interruption to traffic will be happen during heavy monsoons upto certain period of time.
Means, the flow of traffic on all weather roads continue every seasons without any problem.
Fair Weather Roads
Fair Weather Roads is defined as the road which is interrupted during monsoon seasons. Means, during the monsoon, the river or its branches will be overflow across the road. A causeway is a perfect example of fair weather roads.
Also Read : Best Books For Highway Engineering
Classification of Roads based on Carriageway
Road are classified based on carriageway or pavement are listed below.
- Un-paved Roads
- Paved Roads
Un-Paved Road
Un-Paved roads is defined as the type of road which pavement is uneven, not hard and not smooth surface. The earth roads and gravel roads are the perfect example of Unpaved Roads.
Paved Roads
Paved Roads is defined as the type of road which consist the hard pavement, Uniform and smooth surface. The Concrete roads are the perfect example of Paved Roads.
Classification of roads based on Traffic Volume
Based on Volume of Traffic, the roads are classified as Heavy, Medium, and low volume roads. This classification of roads is directly relevant to volume of Traffics.
Also Read: Advantages and Disadvantages of Monolithic Construction
Classification of Roads based on Nagpur Road Plan
The Nagpur Road Plan classified the Indian roads based on location and function are listed below.
- National Highway
- State Highway
- Major District Road
- Other District Road
- Village Road
National Highway
National Highways are the roads which connecting the capitals of large states, major ports, large industrial area, tourist places, foreign highway, etc. Also used for defense & military activity in critical situation.
National Highway allow traffic to flow at higher speed as comparison to state highway. Also provide un-interrupted road communication throughout the country. The national highway in India are expressed in the form of number such as NH-4.
State Highway
State highways are the road of state which connecting the National Highway, district headquarters, commercial area, tourist places, important cities, etc. within state.
The flow of traffic volume in state highway is very similar to national highway. Also the geometric design specification and design speed is same compare to National Highway and State Highway.
Also Read: Precast Concrete Vs Cast in Situ Concrete
Major District Road (MDR)
Major District Roads are the road which connecting the state highway, market places, residential areas, gardens and other important places within cities.
The Major District Road have lower design speed and geometric design specification as compare to national highway and state highway.
Other District Roads (ODR)
Other District Roads are the Rural Roads which connecting the Major district roads, Rural market places, Taluka Headquarters, School, Block development and other main roads. Other District Roads have low design speed and geometric design specification.
Village Roads
Village Roads are the roads which connecting the village for group of village with other major roads. The traffic volume of village roads is very low, that’s why the geometric design specification is also lower. The village roads serve purpose of connecting peoples of villages, farms, schools, etc.
Also Read: What is Slurry Wall Construction
Classification of Roads as per Third 20-Year Road Development Plan
Classification of roads in India was modified in third 20 year road development plan. The roads in India was classified into three groups as per its priority, purpose and function. This three groups are mentioned below.
- Primary System
- Secondary System
- Tertiary System
Primary System
Primary System is the Networks of main roads which is connecting the large states, business hubs, ports etc. The Priority of this system is high.
Primary System consist two category of roads.
- Expressway
- National Highway
Expressway
Expressway are the additional class of road which is added into the third 20 year road development plans.
Expressway consist the superior geometric design specification and high design speed. The traffic volume on expressway is very high. Expressway roads allows vehicles to move very fast.
Expressway is the upper class of national highway which consist extra lanes, very high design speed, safety features, etc.
Secondary System
Secondary system is the network of roads which connecting the expressway, national highways, district, cities, headquarters, etc.
The Priority of secondary system is high to moderate as per its purpose and function. Secondary System consist of two categories roads.
- State Highways
- Major District Roads
Also Read: What is GFRP Bars
Tertiary System
The tertiary system are rural roads and these consist of two categories of roads.
- Other District Roads
- Village Roads
The description related to National Highways, Major District Roads, Other District Roads, and Village Roads is already Discussed on above paragraphs.
Classification of Urban Roads
The Urban area roads are classified as mention below.
- Arterial Roads
- Sub-arterial Roads
- Collector Streets
- Local Streets

