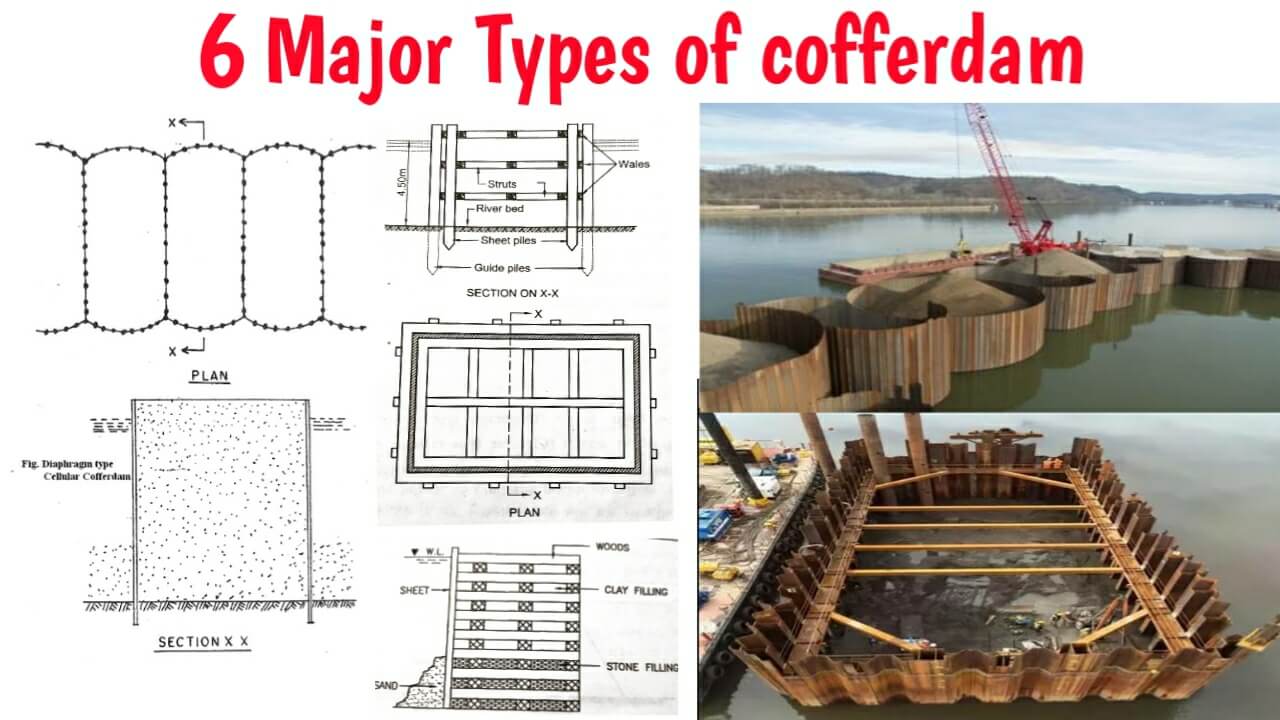
In this article, we explain what is cofferdam. Different types of cofferdam like cellular cofferdam, braced cofferdam, earthen cofferdam, rockfill cofferdam, crib cofferdam, single wall cofferdam, double-wall cofferdam, etc. uses, meaning, methods of cofferdam construction, advantages, and disadvantages.
Table of Contents
What is Cofferdam foundation?
Cofferdam foundation is defined as a temporary structure that is used to prevent soil erosion in the construction area as well as to prevent water from entering the excavated area when excavation is to be done by digging deeper along the river bank or coast.
Which points are kept in mind for cofferdam construction?
The following points should be kept in mind in the cofferdam construction.
- Cofferdam should be watertight as possible. It should be inserted to a hard level in the ground. Often a layer of concrete is laid at the bottom in the cofferdam.
- The design of Cofferdam should be done for maximum water level as well as other destructive forces. Due to that, it is safe in case of bursting, overturning, sliding.
- Water discharged by cofferdam may be above ground or below ground. This water can be shallow or deep, steady, or flowing.
- Materials like clay, wood, steel, and concrete are used for the construction of cofferdam.
- A cofferdam is usually built on the worksite.
Types of cofferdam:
The different types of cofferdams are as follows:
- Earthen cofferdam
- Rockfill cofferdam
- Crib or braced cofferdam
- Single wall cofferdam
- Double wall cofferdam
- Cellular cofferdam
1. Earthen cofferdam:
It is the simplest types of cofferdam. It is used when the water depth is shallow, 1.2 m to 1.5 m and the velocity of water flow is slow.

- In this type of cofferdam, an earth embankment is built around the area to be surrounded. The top width of the embankment should not be less than 1m.
- Its waterside slope 3/2:1 and the inner side slope is kept at 2:1.
- Earth embankment is made from a mixture of clay and sand or clay and gravel.
- Pitching is done by arranging boulder (large stone) on the slope of the waterside to prevent water damage to the embankment.
- Often in the middle of the embankment, Steel sheet piles are inserted to an impervious level of soil below the embankment, to prevent water from entering through the permeable layer of soil.
- The height of the embankment is kept 0.6 m above the water level for safety.
- In the workplace, a drain is kept near the embankment from which water is pumped out.
2. Rockfill cofferdam:
This types of cofferdam is useful when the water depth is up to 3.0 in and the water flow is turbulent. In this type of cofferdam, stones are used instead of clay in the bed. Such cofferdams are cheaper where stones can be easily found.

The disadvantage of Rockfill cofferdam is that it is not impervious. Where the water depth is low, an impermeable layer of soil is spread over the waterside of the embankment.
- Clay particles fill the cavities between the stones and gradually form waterlogged structures.
- The slope of its sides can be kept as wide as 1:1.
- Often the core wall or steel sheet pile inserted between the cofferdam and the bottom of the cofferdam to an impervious level of the soil to prevent water from entering the embankment.
- Core walls are made of clayey soil or cement concrete.
3. Crib or Braced Cofferdam:
This types of cofferdam is made of a wooden cube. The crib is a framework made of wooden horizontal and cross beam alignment. The film is filled with stones, gravel, or clay to increase the stability of the crib against overturning or sliding.

The following conditions are favorable for this types of cofferdam:
- Less workspace.
- The river bed is hard.
- If the water depth is high.
- The water flow is an eddy type.
- Wood is readily available.
4. Single wall cofferdam:
This types of cofferdam is used when the area to be surrounded is small and the water depth is high. Such cofferdams can additionally be used up to a depth of 25 m water.

- Guide piles are inserted on the periphery of the area to be enclosed.
- The spacing of such guide piles is kept at 3m.
- Guide piles are usually made of wood. Steel piles can also be used if the water depth is high. The guide piles are then bolted horizontally at appropriate distances by means of wooden bolts (Wales) bolts.
- Then sheet piles are applied with a strut and bracing. Wood sheet piles are used for water depth up to 10 m, steel sheet piles for water depth more than 10 m.
- On the inside and outside of the sheet, half-filled bags of sand are rocked to increase the durability of the cofferdam.
- Water is pumped out of the enclosed area and foundation work is started.
5. Double wall cofferdam:
A single wall cofferdam is costly when the enclosure area is large and the water depth is high. as the. The thickness of the components like sheet piles Strut, Wales, etc. is much more required to withstand water pressure. In such a situation a double-wall cofferdam is useful.
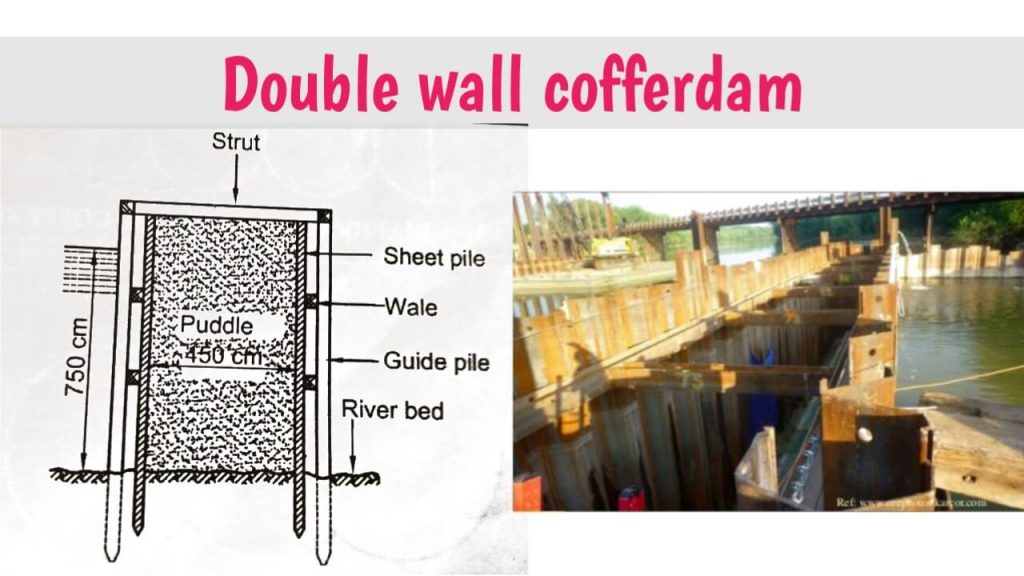
There are two types of double wall cofferdams:
- Ohio type cofferdam
- Wood or steel sheeting cofferdam with Wales and tie rods.
i. Ohio type cofferdam:
This type of cofferdam is called Ohio river type wood sheeting cofferdam. As it was first used for construction over the Ohio River in the United States. It can be built very cheaply and quickly.
It is used in hard layers where erosion is unlikely. Such cofferdams are suitable for deep water or fast water flow.
6. Cellular cofferdam:
This type of cofferdam is useful when the enclosure area is large and the water depth is high. Cofferdams are used in the construction of water structures such as boilers, pushes, etc.
There are two main types of cellular cofferdam:
- Circular type cellular cofferdam
- Diaphragm cellular cofferdam
i. Circular type cellular cofferdam:
In Circular Cofferdam, circular cells are inserted into the ground to a certain depth above the boundary area.
Such a cell is connected by an arc of a circle. The radius of such an arc is 2.5 m. The arc forms an angle of 30° to 45° instead of contact with the circular cell. The cell is filled with clay, sand, or gravel.

The advantages of Circular type cofferdam are as follows:
- Each cell can be filled to the head independently before the construction of the second cell and in this way, the construction of the second cell is not distorted so the construction of the cell can be started from a different point.
- Each cell behaves as a self-supporting independent unit.
- Less steel per unit length is used in the construction of a circular cell compared to a diaphragm type cell.
Cellular cofferdam is suitable for heights of 10 to 15 m. The diameter of the cell is kept from 10 to 15 m and the distance from the center to the center is kept from 12 to 18 m. The bottom of the river is hard rocky and the top layer of clay or silt is more suitable for such cofferdam.
ii. Diaphragm type cellular cofferdam:
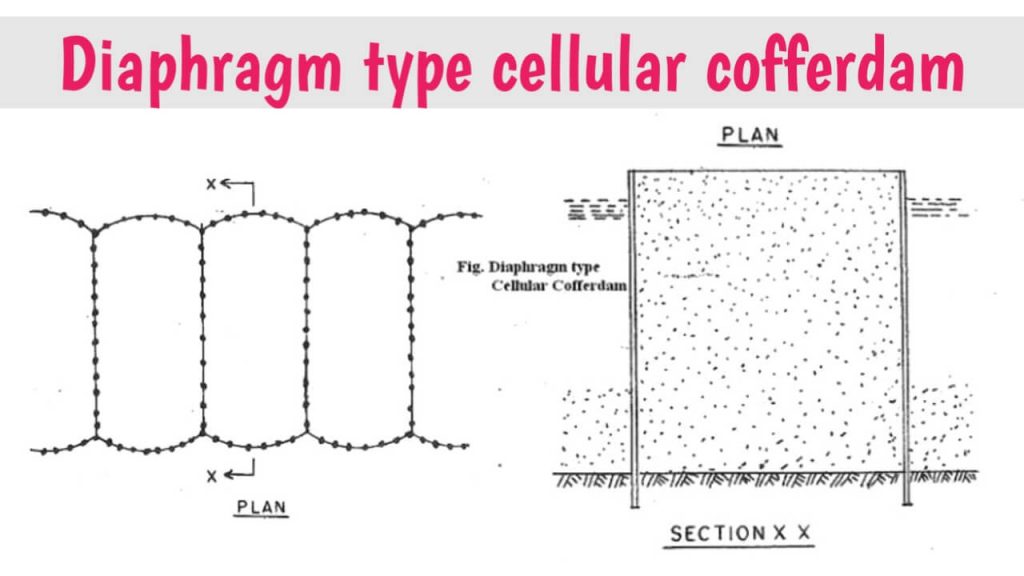
In this type of cofferdam, steel sheet piles are attached to each other to form a series of arcs. Straight walls are attached to each other with the arc of sheet piles on both sides. Usually, the radius of the arch is kept equal to the distance between the two diaphragm walls.
In order to create uniform tension between the diaphragm and the arch, building materials like sand, gravel etc. are filled in it after immersing the cell in water to the required depth.
In all cells the filing of material should be done at the same rate up to the same height so as not to wrap the diaphragm.
Factors affecting selection of cofferdams construction:
Cofferdams can be of different types. But what kind of cofferdam to build in which place depends on the following things:
- The area to be protected by a cofferdam, i.e. small area or large area.
- The height of the water at the place where the cofferdam is to be constructed i.e. shallow water or deep water.
- The state of water i.e. water is steady or flowing.
- The type of velocity of water flow i.e. water flows with slow velocity or fast velocity.
- Type of soil at the bottom of the cofferdam, Pervious layer, or Impervious layer.
- Availability of Materials at work.
- The possibility of floods as well as tides and their height.
- Increase inflow velocity due to obstruction of water flow from the construction of Cofferdam and the possibility of erosion of bottom.
- Facilitation of transport of materials and machinery required for of Cofferdam construction.
Necessity of cofferdams:
The need of cofferdams construction arises in the following situations:
- When construction is to be done on the banks of a dry or watery river or between rivers.
- When construction is to be done on the beach.
- When construction is to be done in the middle of the lake or on the shore.
- When deep excavation is to be done at a place of deep granular soil.
- When deep excavation is to be done on clay soil.
- When excavation is to be done below ground level.
- When there is a possibility of landslides due to deep excavation.
- When private or government property is located near the excavation.
- When water is likely to seep into the excavation from the surrounding area.
Uses of cofferdams:
- To facilitate the work of laying piles in the ground.
- Laying of raft and mesh foundation
- Laying of Grillage foundation.
- To construct the foundations of embankments, piers, and abutments.
- Surround the work area and prevent water from entering the space.
- To provide a working platform when water leaks during the foundation excavation of buildings.
- To take out a submerged ship from water and to encircle the place.
- To provide working space without damaging the surrounding structures such as buildings, pipelines, sewer line etc.
- To construct the foundation and top of the concrete dam.
Download pdf of what is cofferdam? Types of cofferdam | uses | necessity
Also read:
- What is caisson foundation? types | Uses | construction methods
- 7 Best method of dewatering || procedure || necessity

I am a Professional Civil & Structural Engineer having more than 4 years of experience in Engineering, Procurement and Construction industry. Here i sharing the latest updates of EPC Projects and Construction News.