 |
| Image Source – Google | Image By –PolREFF |
Table of Contents
Definition or meaning Thermal Insulation in construction or building:
Building inside temperature is a major factor for comfortable living. In a hot climate region or cold climate the region, maintaining inside temperature of the building is essentially required which is obtained by proper thermal insulation of a building.
Therefore the method which maintains the constant (comfortable) temperature inside the building by the help of different material, a method is known as thermal insulation of building and material used for thermal insulation purposes is known as a thermal insulator.
Benefits of thermal insulation:
- Comfort: Thermal insulation allows the room to cool in the summer and warm in winter so that it can be enjoyed in both seasons.
- Fuel Saving: Reduces heat transfer indoors and outdoors due to thermal insulation. Therefore, less electricity is needed to operate the air conditioning unit or fan
- Condensation: Condensation means moisture on walls and ceilings. Condensation occurs when hot air exposed to cold walls. Therefore Condensation phenomena are reduced by the help thermal insulation.
- Water system: In the winter water pipes do not freeze due to thermal emulation and heat is not wasted in the hot water system.
What is the material used as thermal insulation in building construction?
The materials used for thermal insulation areas follows:
1. Rock wool
Rock wool, which is additionally called rock wool, comes in easy-to-install batts, almost like fiberglass. But rather than being composed of fluffy glass fibers, mineral wool is formed of you guessed it rocks, which doesn’t even seem possible. Here’s a quick explanation of the manufacturing process.
 |
| Rockwool |
Natural rock is heated during a furnace to about 3,000 degrees until it melts into a liquid. The magma-like liquid is exposed to a high-pressure jet of air or steam, then spun at super-high speed into long fiber strands. (Think: spun sugar machine stuffed with liquid rock.) The strands are captured and compressed into thick, dense mats, which are then you convenient-sized batts of insulation.
- Made from natural, sustainable material
- Typically contains up to 75 percent recycled content
- Retains heat well and traps air, which slows the transfer of warmth
- Non-combustible and fire resistant to about 1,400 degrees
- Highly water repellent
- Excellent sound-deadening properties
- Higher insulating value than fiberglass
- Long-term performance—rock wool doesn’t degrade over time
- Allows moisture to flee (which deters mold and mildew).
2. Corkboard slabs
- Cork is obtainable within the shape of boards or granules. Corkboards are especially suitable for insulating walls, roofs, and floors. The granules, on the opposite hand, function as an appropriate insulation material for cavity walls, floors or screed.
- Thanks to its damp-proof properties, cork is applicable in environments where there’s a risk of damp penetration (e.g. roof constructions, the cavity,…).
- There is no got to wear protective clothing during the installation. As cork doesn’t cause irritation or dust, it’s not harmful to health.
3. Slag wool
- Slag wool could be a manmade vitreous fiber made by spinning slag into insulating fibers. Some Rockwool producers use closely pure recycled steel slag.
- Mineral wool insulation, developed in 1850, patented in 1875 in the U.S. and this material, also called mineral wool or in some texts slag wool insulation remained in popular use within the U.S. up to the 1950s, and remains in use today (2008) in some new construction, in manufactured housing, and in special applications like the insulation of low-slope roofed cathedral ceilings and scissors-truss roofs.
4. Fibers boards
 |
| Image Source – Google | Image By –IndiaMart |
- fiberboards insulations are mineral or also referred to as ceramic fibers, including alumina and silica and bonded with extremely high-temperature inorganic binders, or a mechanical interlocking of fibers eliminates the need for any binder. The
- material is manufactured during a blanket or rigid form. Thermal shock resistance is high. Temperature limits reach
- 1750°C. the fabric is non-combustible.
For More Building Insulation technique and Service visit : Shield’s insulation services available throughout the country
5. Flexible blankets
- the flexible blanket is Available as glass, fiber, rigid board, pipe covering and other pre-molded shapes. the flexible blanket is served temperature range is -40°C to 232°C. the flexible blanket is neutral. however, the binder may have a pH factor.
- The product is non-combustible ( if the glass is used) and has good sound absorption qualities.
6. Foam plastic
- Insulations produced from foaming plastic resins create predominately closed cellular rigid materials. “K” values decline after initial use because the gas trapped within the cellular structure is eventually replaced by air. Check manufacturers’ data. Foamed plastics are lightweight and also have excellent cutting characteristics. The chemical content varies with each manufacturer. Available in pre-formed shapes and boards, foamed plastics are generally utilized in the lower intermediate and therefore the entire coldness ranges. Consideration should be made for fire retardancy of the material.
7. Aluminum foils or thermal insulation sheet or thermal insulator for roof
- This is a replacement environmentally-friendly Heat Insulation material, which is soft, light and straightforward to put in. It is made up of aluminum foil and polyethylene by special machinery. It has no odor and toxicity. It not only overcomes the discomfort and environmental effect brought by insulation material like glass fiber and epis-plastic materials but can also resist the ultraviolet which can penetrate through the plate, concrete, wood, and other common heat insulation materials. aluminum foil insulation material not only has good insulation, heat reflection & insulation, and anti-radiation functions but also has good moisture-barrier, heat preservation and energy-saving functions in housing construction (roof).
8. Lightweight concrete
9. Sawdust
10.Gypsum board
11. Wood shavings
12. Asbestos cement board
13. Chipboard
14. Foam glass
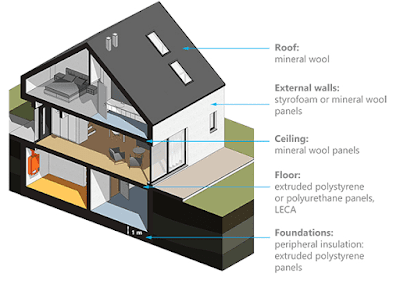
How to do thermal insulation of foundation in the building?
- The most effective way to insulate elements of the building that is in contact with the ground is to use the so-called perimeter insulation. It is external, continuous insulation freed from thermal bridges used for the building partitions that are in direct contact with the bottom.
- Installing thermal insulation on the external surfaces of basement walls eliminates the danger of freezing temperatures penetrating the walls and prevents moisture from condensing inside the building. The role of the peripheral insulation isn’t only to scale back heat loss but also to guard the external waterproofing against damage.
- Material use:- Extruded polystyrene plates 5 to 10 cm thick
How to do thermal insulation of the ground floor in the building?
- In order to satisfy the thermal insulation standards the bottom floor should be built as a layered construction; flooring, under layer, appropriate insulating layers and base.
- Before laying the ground it’s important to get rid of about 30cm of the topsoil and replace it with a 5 to fifteen cm layer of sand or rubble. Then a ten cm layer of concrete is poured followed by a 2.5 cm layer of waterproof cement or other hydro insulation. The thermal insulation goes on top.
- The material has got to be immune to high with good thermal insulation and hydrophobic properties. Boards of extruded polystyrene, polyurethane plates and concentrated LECA coated with cement about 1 cm thick are used for this purpose. A sheet of plastic sheeting is spread across the insulation. Not only does it separate and secure the layers but it also provides lubrication for the bottom.
- Material use:- Extruded polystyrene plates 3 to 5 cm thick, Polyurethane plates 5 cm thick, LECA about 1 cm thick
- The light wet method supported rock wool and expanded polystyrene. because of its low cost, good durability and easy installation this method is most ordinarily used to insulate exterior walls. It will be used to insulate walls made from bricks, airbricks, aerated concrete, and concrete monolithic or prefabricated walls. Another convenient characteristic of this method is that the walls will be plastered or left unfinished.
- Insulation using the low wet method is predicated on attaching the insulant with glue and mounting pins to the outside surface of the wall, covering it with a skinny layer of mortar with a reinforcing mesh and finished with a layer of plaster. the fundamental insulating elements are rock wool and expanded polystyrene. the outside of the house must be insulated all the high to the upper edges of the parapet or elbow walls. rock bottom a part of the insulation must be aligned with the highest edges of the basement windows. The plinths must even be insulated.
- It is also vital to insulate the outside surface of the window, openings to stop freezing and mold growth inside and around the frame.
- Material use:- Styrofoam 10 to 25 cm thick, Mineral wool plates 10 to 25 cm thick
How to do thermal insulation of the ceiling in building construction?
- Ceilings between two residential floors or between the attic and therefore the room is most ordinarily insulated because of acoustic requirements and fire safety. In this case, insulator provides soundproofing slows down the spread of fireside and reduces heat loss from rooms.
- Material use:- Mineral wool boards 5 to 15 cm thick
How to do thermal insulation of Roof in building construction?
- A poorly insulated roof can cause up to 10-15% of heat- loss. this is often why it’s an important element for the correct thermal insulation of a house. the kind of insulation depends on the structure of the roof. Insulating a flat roof is different from insulating a pitched roof.
Image Source – Google | Image By –PURIOS - Key factors for insulating pitched roofs are:
- high thermal insulation, dependent on the thickness of the layer and thermal conductivity,
- high thermal insulation, hooked into the thickness of the layer and thermal conductivity, tightly sealed with no thermal bridges,
- the insulation material should fill the insulated surface tightly,
- effective protection against moisture,
- windproof so as to stop infiltration of outdoor air and escape of warm air, while allowing moisture to go through,
- fire resistant so as to make a barrier against spreading flames,
- good acoustic properties,
- easy to put in.
- It is important to understand that insulation puts additional pressure on the roof structure. this is often why the insulation material must be light enough to not strain the existing structure and avoid the owner having to make an expensive, heavy structure.
- Due to these requirements, the simplest solution is glass wool. Not only is it warm but also very elastic which helps to seal the surface very tightly. the insulator is extremely light so it doesn’t strain the roof structure. it’s worth remarking that so as to insulate a mean 150 m2 pitched roof with an insulator, 450 kg of fabric is required. Insulating an equivalent roof with the lightest available rock wool would require 900 kg of the fabric.
- Hard rock wool boards are wont to insulate flat roofs. To insulate ventilated roofs the foremost commonly used materials are mats and granulates of rock wool and sometimes boards.
- Material use :- Glass wool layers 15 to 30 cm thick, Glass wool layers 15 to 30 cm thick, Granules of mineral wool 15 to 35 cm thick
ALSO READ :-



Hello Sanjay. Nice article! I am not quite familiar with thermal insulation. I only heat it from my mom. Now that I plan to build my own house, I got curious about how it would benefit my property. So, it’s the perfect time to find your post. I like that you have included each insulation material’s key characteristics and how to insulate different parts of a building. But which material is the most eco-friendly?