We explain what is shallow foundation, various types of shallow foundation like an inverted arch footing, raft foundation, grillage foundation, combined footing, strap footing and so more. where it is used. for different types of construction and soil properties, it is necessary to understand which type of shallow foundation should be used.
| Like us on Facebook | Click Here |
| Join our Telegram Group | Click Here |
| Subscribe us on YouTube | Click Here |
| Follow us on Google News | Click Here |
Table of Contents
What is Shallow Foundation?
Shallow foundation is defined as a foundation which Width is greater than its depth or equal. that type of foundation is known as the shallow foundation, which is commonly used in load-bearing construction.
Types of shallow foundations:
Various types of shallow foundation are given below.
- Spread Footing
- Combined Footing
- Cantilever Footing or Strap Footing
- Raft or Mat Footing.
- Grillage Foundation.
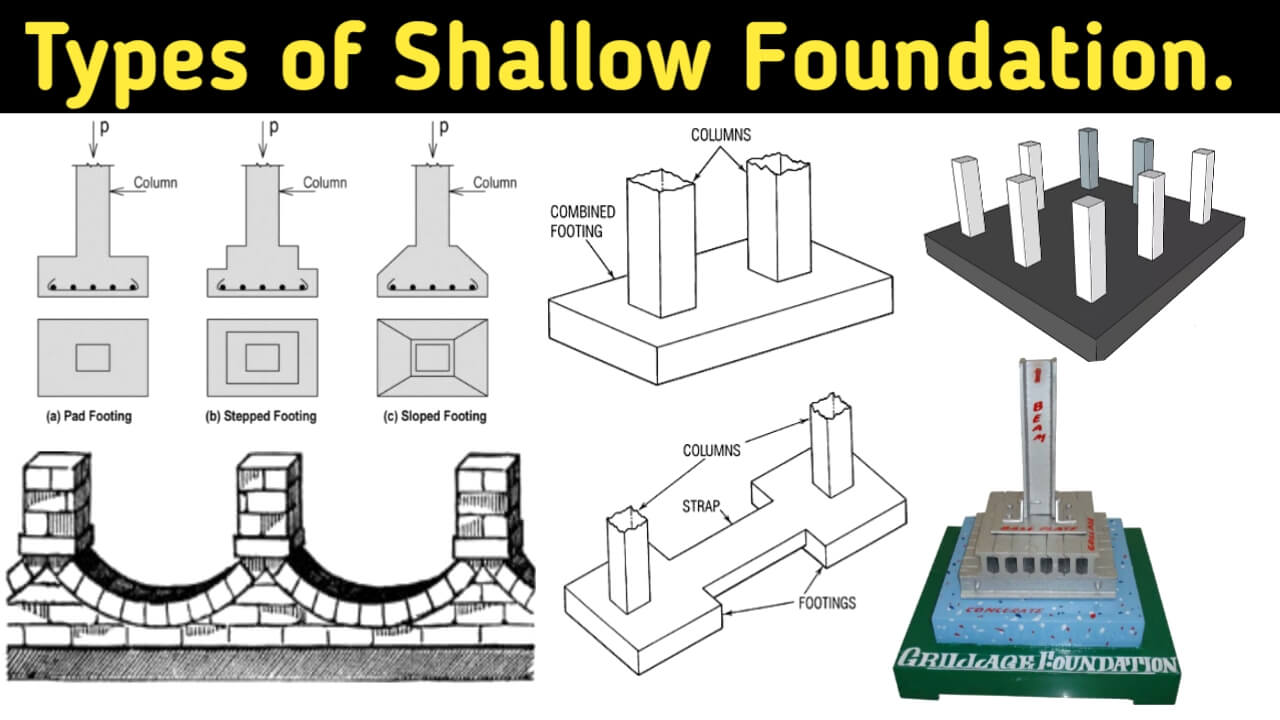
1. Spread Footing:
What is spread footing?
The spread footing is one types of shallow foundation. In this type of foundation, the lower part of the foundation is gradually widened. So that the load of the structure is distributed over a large area and the intensity of the load on the base.
Where spread Footing is used?
When the building is not a multi-storey, load of column is less and, soil bearing capacity is meet in less depth in this case the spread footing is commonly used and it is economical.
Why spread footing is important?
Spread footing is important in a view of cost. Because it is economical compare to other foundations.
Different Types of spread footing :
- Wall footing
- Reinforced concrete footing
- Inverted arch footing
- Column footing or Isolated footing
i. Wall footing:

- The bottom of this type of shallow foundation is paved with a layer of Brick Bat cement concrete (BBCC) 1: 3: 6. The width of this layer is kept three times of the wall thickness. It is also often called strip footing.
- The layer thickness of the BBCC should be twice the projection on both sides.
- The width of the lowest layer of masonry is kept to be 2 times of plinth level wall thickness.
- The height of the bricklayer is 10 cm.
ALSO READ: 8 aspect to make earthquake proof masonry construction.
When the wall is under heavy load or the soil bearing capacity is low, then the width of the base of the wall (2 times wall thickness + 2 times projection) is required. So that the width of the masonry increases and the load can be transferred over a large area of concrete.
ii. Reinforced concrete footing:

The reinforced concrete footing is also one type of shallow foundation. The size of wall footing is greatly increased when the wall is under heavy load and the bearing capacity of the soil is low.
In such a case it is advisable to place rainforest concrete footing under the wall. Such footing reduces the amount of masonry. Costs also decrease. A layer of concrete 7 to 8 cm thick is laid under the reinforced footing.
iii. Inverted Arch Footing:

- An inverted arch is built between two pillars in this type of foundation. Rise of the inverted arch is kept equal to 1/5 to 1/10 of the span.
- Inverted arch should be built into the cement mortar.
- The lateral pier should be designed to withstand the pressure externally due to arch action. The inverted arch reduces the depth of the base. So this foundation is economical in soft soil.
- This method is less used in the foundations of buildings. But more suitable for bridges, tanks, drainage line supports etc.
- Inverted arch footing is more suitable for Soft soil.
Also Read: What is GFRP Bar | GFRP Bars vs Steel Bars
iv. Column footing or Isolated footing:

- This type of footing is used for separate columns.
- It is also called isolated footing.
- Such type footing bases are round, rectangular or square.
- Such type footing bases are Simple, Stepped or Sloped type.
- For heavily loaded columns, reinforcement is placed in both directions in the concrete bed. For RCC columns, offset of 15 cm is maintained on all four sides of the concrete bed.
2. Combined Footing:

- A combined footing is also one common types of shallow foundation which is mostly used.
- A combined footing is used for two columns.
- They are rectangular or trapezoidal in shape.
- The rectangular footing is used when the load on both columns is the same and trapezoidal footing is used when the load on both columns is unequal.
Combined footing is used in the following cases:
- When two adjacent footings overlap.
- When a column is very close to the property line and footing is putting on the property line then the footing is eccentrically loaded. In this case use this footing.
3. Cantilever footing or Strap footing:

This type of footing prepared by combining two RCC Footing with RCC strap. The RCC strap only acts as a beam connecting the two footings. It does not take soil reaction from below.
Where cantilever footing is used?
When the distance between the two columns is greater and the allowable soil pressure of the soil is higher, strap footing is cheaper than combined footing.
Also Read: What is Monolithic Construction Technology
4. Raft or Mat foundation:

This types of shallow foundation, filling RCC slab over the entire construction area or some part of it. Many columns, walls are supported on this slab. This type of shallow foundation is used large quantity of concrete.
Where raft foundation is used?
- The soil bearing capacity is low.
- The soil is prepared by filling.
- Columns and walls are close and its footing overlaps.
- The soil is non-homogenous soil with soft soil pockets.
- Differential settlement is likely to occur.
- There is a lot of variation in the load on different columns.
5. Grillage Foundation:

- Grillage foundation is used when the load on the column is very high and the bearing capacity of the soil is low.
- Deep digging can be avoided with this type of shallow foundation.
- A concrete layer of about 20 cm thickness is laid by digging to the required depth.
- Rolled steel joists (RSJ) are arranged on top of the concrete layer, with a gap between the flanges of the two RSS, 1.5 to 2.0 times the width of the flange or 30 cm whichever is less.
- The second level of RSS is arranged perpendicular to the first level of RSJ.
- The space between the RSJ is filled with concrete. The end of the RSJ should have at least 8 cm concrete cover.
- The concrete filled in the gap between the RSJ does not take any kind of load, it just Saves RSJ against to corrosion.
- In both layers of RSJ beam, it is attached with a spacer bolt to maintain the spacing of the beam.
- The base plate is placed on the top most layer of the RSJ and a steel column is built on it.
Types of shallow foundation PDF download

I am a Professional Civil & Structural Engineer having more than 4 years of experience in Engineering, Procurement and Construction industry. Here i sharing the latest updates of EPC Projects and Construction News.